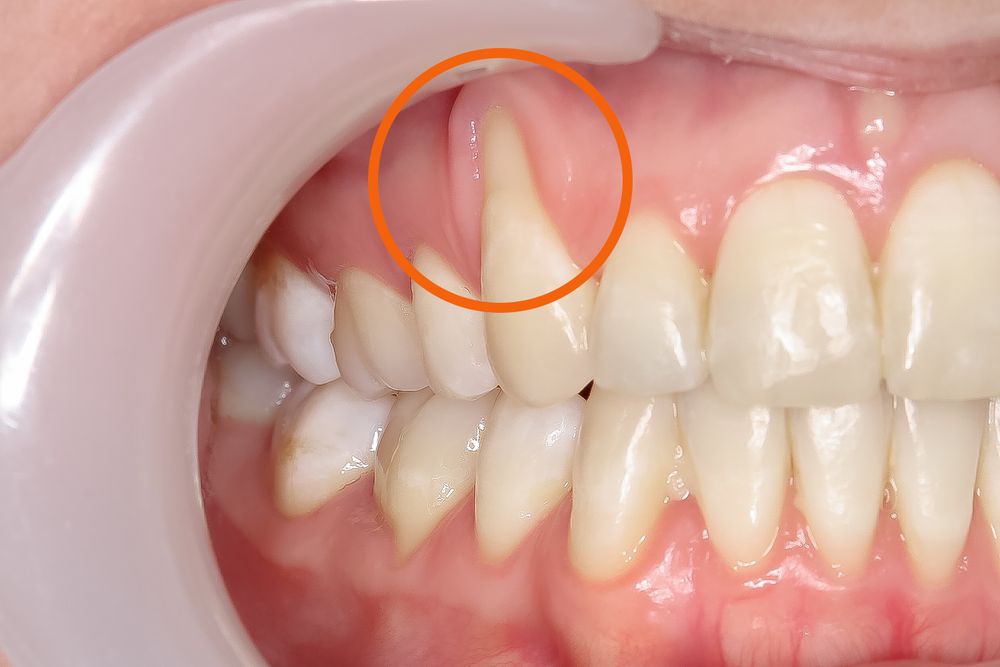
Gum recession occurs when gum tissue retreats from the teeth, revealing the underlying roots. Various factors contribute to this, such as vigorous brushing, smoking, and genetic predisposition. Treatments encompass antibiotics, antimicrobial mouth rinses, and surgical interventions. Although gum recession is irreversible, these treatments aim to halt its progression and prevent further deterioration.
What is gum recession?
Gum recession, a type of gum disease, occurs when the gum tissue recedes from the teeth, uncovering the underlying roots. This exposes teeth to heightened susceptibility to cavities. Increased sensitivity during brushing or eating can also accompany this condition. Gum recession varies in severity, ranging from mild to moderate or severe, and it can impact a single tooth or multiple teeth.
Who does gum recession affect?
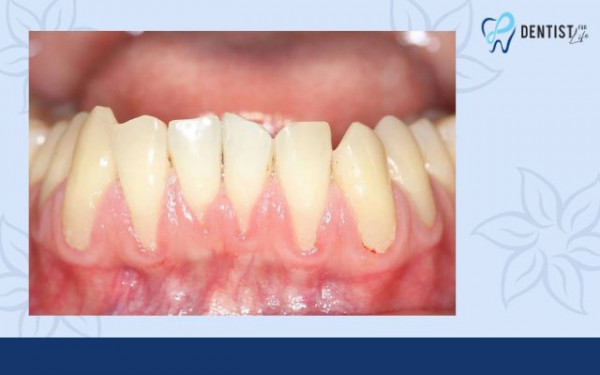
Although gum recession can impact individuals across all age groups, it predominantly occurs in individuals aged 65 and older. The likelihood of experiencing recession increases if you have a history of periodontal disease, underwent orthodontic treatment like braces, use chewing tobacco, have lip or tongue piercings, or practice aggressive tooth brushing.
See more: Expert Guide to Wisdom Tooth Extraction
Symptoms and Causes
What are the symptoms of gum recession?
The most evident indicator of gum recession is the exposure of the tooth root. Additional warning signs of gum recession include discomfort or pain near the gum line, heightened sensitivity to hot, cold, or sugary foods, as well as while brushing, flossing, or during dental cleanings.
If left untreated, gum recession can lead to severe oral health issues like bone loss, tooth mobility, or even eventual tooth loss. If you observe any of these symptoms, promptly schedule an appointment with your dentist for assessment and necessary treatment.
What causes the recession of gums?
Gum recession may occur due to various factors, encompassing aggressive brushing habits, the buildup of dental plaque or tartar, periodontal disease, gum tissue trauma, tooth misalignment, tobacco use, and lip or tongue piercings.
While inadequate oral hygiene often contributes to this condition, genetic predisposition to thin gum tissue is also a common cause.
Regardless of the underlying reason for gum recession, timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment play vital roles in averting potential long-term oral health issues.
FAQ
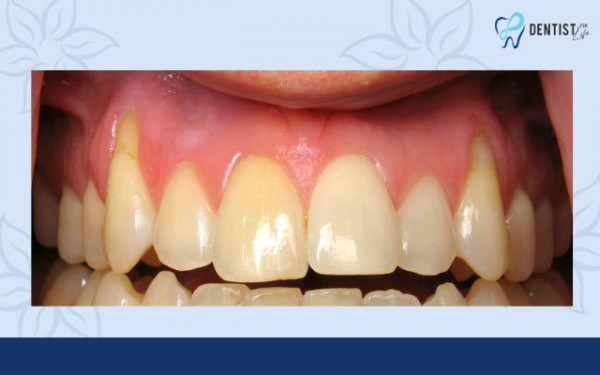
Can gums grow back?
Regrettably, gums once receded cannot regenerate. However, there are measures you can adopt to prevent further deterioration of the gum recession.
How can one alleviate sensitivity resulting from gum recession?
Individuals experiencing gum recession often encounter discomfort or pain due to the exposed tooth roots lacking the protective enamel, instead covered by less resilient cementum. Dentists may employ fluoride varnish or other desensitizing agents to alleviate the associated discomfort. Additionally, using desensitizing toothpaste at home can prove beneficial. During dental cleanings, dental hygienists can also employ numbing agents to enhance patient comfort.
What’s the best toothpaste for gum recession?
The optimal toothpaste for gum recession addresses discomfort and sensitivity. Effective choices include desensitizing toothpaste containing active components such as potassium nitrate, stannous fluoride, arginine, or strontium chloride. These ingredients are specifically designed to soothe the nerves within your teeth. For best results, consistent long-term use is recommended, although it may take several weeks before the toothpaste’s effects become noticeable.
How do they fix receding gums?
Treating receding gums varies based on its cause. Minor cases might benefit from non-invasive methods like topical antibiotics, dental bonding, or orthodontics. Yet, often, full correction necessitates gum recession surgery in most instances.
See more: Discovering the True Teeth Whitening Cost: What You Need to Know
Is it possible to prevent a gum recession?
While gum recession might not always be avoidable, especially if you have a genetic predisposition to thin gum tissue, you can significantly minimize the risk of recession caused by infections by practicing proper dental hygiene.
This includes thorough brushing of your teeth twice daily, daily flossing, using antimicrobial mouthwash twice a day, and adhering to your dentist’s recommendations for teeth cleanings. Most individuals maintain healthy gums with biannual cleanings, although some might require more frequent visits.
Opt for a soft-bristled toothbrush, refrain from smoking or using chewing tobacco, and promptly consult your dentist if you observe any signs of gum recession.