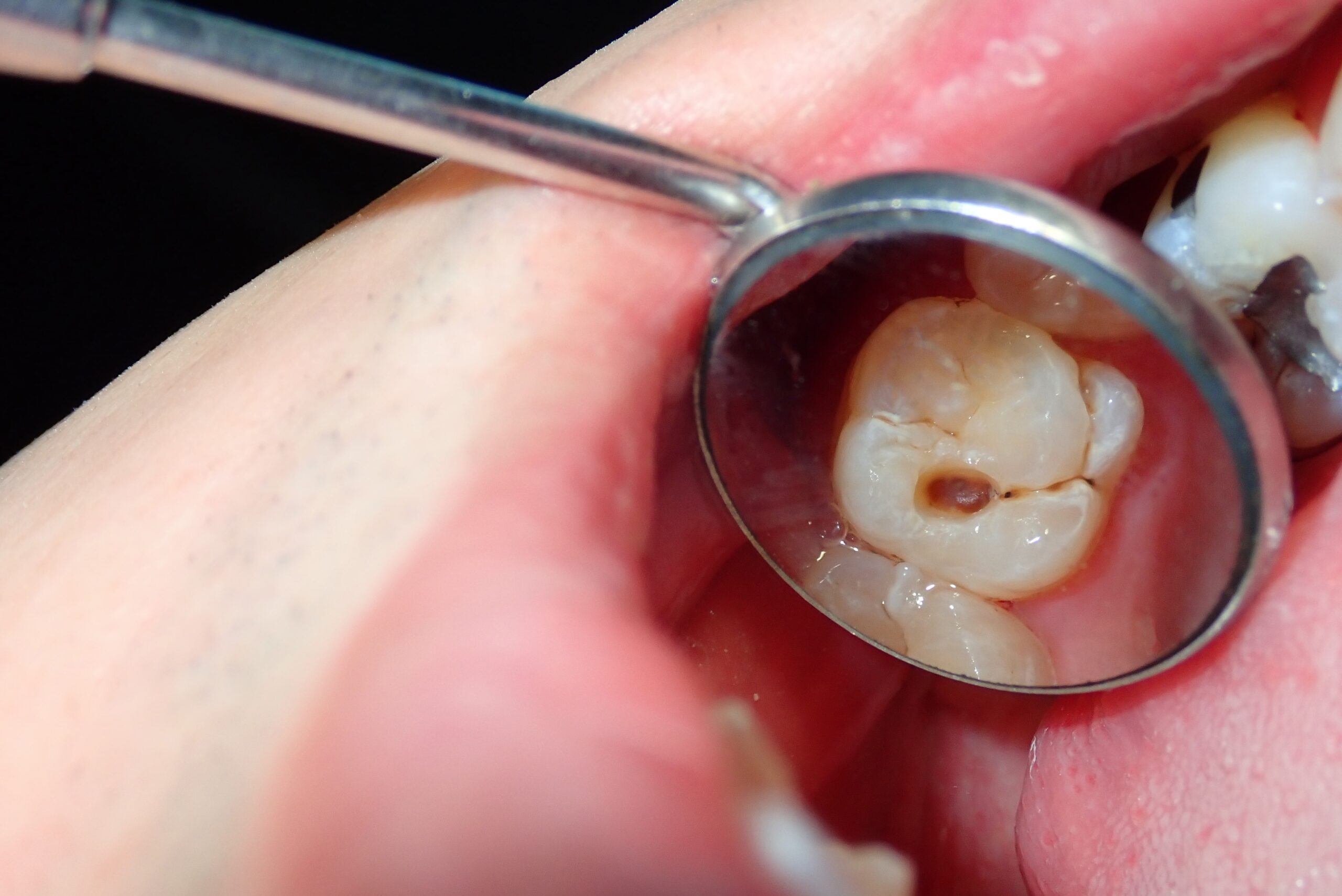
Curious about the early signs of dental cavities? You’re not alone. It’s important to maintain good oral health and part of that is knowing what to look for when it comes to dental issues. In this guide, we’ll explore “what does a cavity looks like“ at different stages so you can recognize them.
What Is a Cavity?
A cavity is a small hole that forms in a tooth. If left untreated, the cavity can progress from the surface of the tooth to the dentin, which is the bony tissue beneath the enamel, and the nerves connected to the tooth. This can lead to severe pain and potential infection, resulting in an abscess, and a pocket of pus around inflamed tissue.
It is possible to have multiple cavities in a single tooth, and cavities can occur in any tooth, including baby teeth. Cavities can affect people of all ages, from infants to senior citizens.
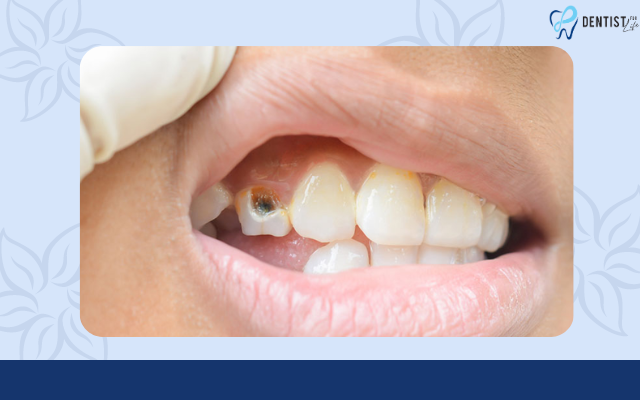
What does a cavity look like in the early stages?
Early-stage cavities may initially present as small brown stains or spots, which can be difficult to detect, especially in the crevices of molars. Recognizing these signs can prompt early intervention to prevent further deterioration.
When in their initial stages, cavities may manifest as small white or chalky spots on the tooth’s surface, often barely discernible to the untrained eye.
They can develop on any tooth surface, including molars and front teeth, and may also form between teeth, making them challenging to identify without dental X-rays. Early cavities may also have a slightly rough texture when felt with the tongue, indicating the need for prompt attention to prevent rapid progression.
Cavities are a significant health problem and expense
Dental cavities, also known as tooth decay or caries, represent a pervasive and irreversible form of tooth damage. This issue is a significant public health concern in the United States and globally. The US Centers for Disease Control (CDC) has provided compelling statistics:
- Roughly 1 in 6 children aged 6 to 11 have experienced at least one cavity.
- More than 25% of adults have untreated cavities.
- Approximately 1 in 6 individuals over the age of 65 have lost all their teeth. Smokers are three times more likely to experience tooth loss.
- Each year, over 34 million school hours are lost due to dental emergencies.
- An estimated 45 billion in productivity is lost annually to oral disease.
- In 2018, the US spent 136 billion on dental care, encompassing cavity diagnosis and treatment.
See more: Tooth extraction healing stages
What Causes Cavities?
Cavities are primarily caused by the combination of bacteria in the mouth and a diet high in sugary foods and drinks.
Formation of Plaque
Plaque formation occurs when bacteria in the mouth combine with sugars and starches from food to produce acids. These acids can attack tooth enamel and lead to tooth decay. It is important to maintain good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, to prevent plaque buildup.
Attack of Plaque
When plaque is allowed to accumulate on the teeth, it can lead to various oral health issues. The acids plaque produces can cause tooth decay, gum disease, and bad breath. To defend against the attack of plaque, it is crucial to practice consistent oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups.
Remember, prevention is the key to maintaining a healthy smile!
Destruction of the Tooth
If plaque buildup is not effectively removed, it can continue to attack the tooth enamel, leading to further decay and potential tooth loss. The acids produced by plaque can erode the enamel, causing cavities and weakening the structure of the tooth. To prevent further destruction of the tooth, it is important to seek professional dental care and follow a consistent oral hygiene routine.
Remember, early intervention and regular dental check-ups are essential for maintaining optimal oral health!
See More: Teeth Whitening Cost
Cavity Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing cavities:
- Poor oral hygiene habits
- High consumption of sugary and acidic foods and drinks
- Dry mouth
- Lack of fluoride exposure
- Dental enamel defects
- Infrequent dental visits
It is important to be aware of these risk factors and take appropriate measures to prevent cavities, such as practicing good oral hygiene, reducing sugar intake, and visiting the dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings.
How Are Cavities Treated?
Tooth removal
Extraction may be necessary if a cavity has extensively damaged a tooth. Additionally, when a large cavity affects a baby tooth that is close to naturally falling out, extraction may be considered. However, our primary goal is to conserve the remaining tooth structure whenever possible. This approach minimizes discomfort, reduces costs, and promotes better oral function and structure.
Filling
Different types of dental fillings offer various benefits and drawbacks:
- Cast gold fillings are durable and strong, but they are expensive and time-consuming to place. Additionally, they do not match the natural tooth color.
- Silver (amalgam) fillings are relatively inexpensive and durable, but they look unnatural and may contain trace amounts of mercury. They also require extra space in the tooth.
- Tooth-colored composite fillings are the best choice for matching teeth and can be used with chipped or broken teeth. However, they wear out faster and cost more than silver fillings.
- Ceramic fillings, usually made of porcelain, resist staining but are as expensive as gold fillings.
- Glass ionomer fillings, made of acrylic and glass, can be used around nerves, below the gum line, and with very young children.
Before applying the filling, the dentist numbs the area around the tooth to eliminate pain. Then, the decayed area of the tooth is removed with a fine dental instrument. The area is cleaned, and sometimes a protective covering is applied to the nerve. Once the filling is in place, it may need to be cured for a short time if it is a composite filling. As a final step, the filling is trimmed and polished.
See more: Restorative Dentistry Near Me
Can You Prevent Cavities?
Preventing cavities is possible with consistent oral hygiene practices. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using mouthwash can help remove plaque and prevent decay. Additionally, limiting sugary and acidic foods and drinks, and visiting your dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings are essential for cavity prevention. Taking these steps can help maintain good oral health and reduce the risk of developing cavities.
Tips for Cavity Prevention and Maintenance
To prevent cavities, follow these steps: brush and floss regularly, visit your dentist for check-ups, maintain a balanced diet, consider fluoride treatments, and get dental sealants for added protection.
Conclusion
In conclusion, preventing tooth decay is crucial for maintaining good oral health and avoiding painful and costly dental problems. At Dentist For Life, we prioritize educating our patients on effective oral hygiene practices and providing preventative care to reduce the risk of tooth decay. By working together, we can help you achieve a healthy and beautiful smile for life. Don’t wait until tooth decay becomes a problem – schedule an appointment with us today and take the first step towards a healthier smile.