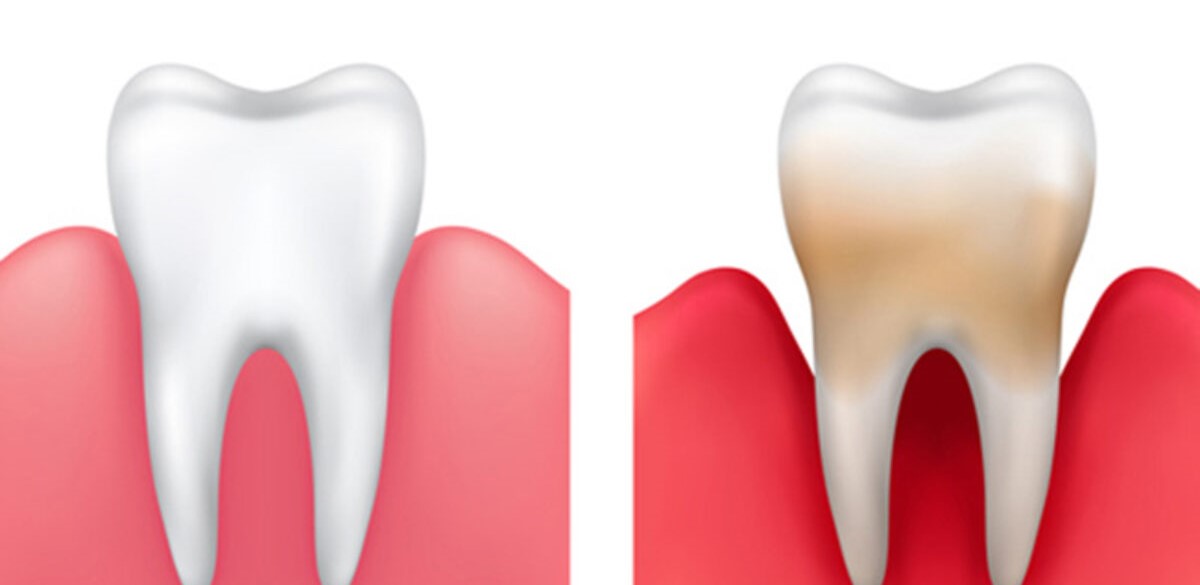
Periodontics, a specialized branch of dentistry, centers on the well-being of gums and the jawbone, crucial tissues that provide support to your teeth. A periodontist, a specialist in gum health, undergoes extensive training for three additional years focused specifically on periodontics following the completion of a four-year dental school program.
What is periodontics? The cause of the illness?
Periodontitis is an inflammatory condition of the tissues surrounding the teeth, affecting the supporting structure of the teeth, causing them to lose connection with this supporting tissue. Periodontitis initially only affects the soft tissue – the gums – and can later progress to affect the bone that plays an important role in holding the teeth. In severe cases, periodontitis can cause tooth loss.
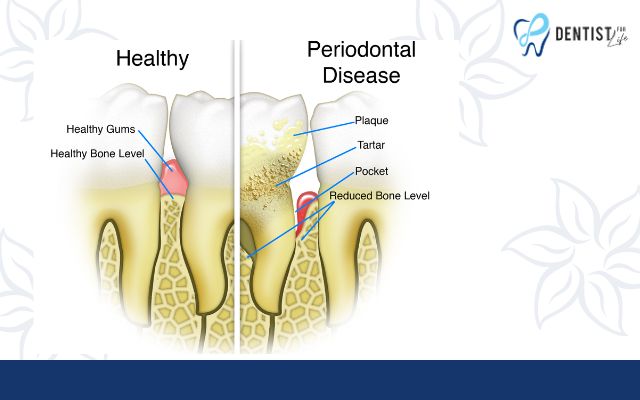
Causes of periodontal disease
Periodontitis, also known as gum disease, is primarily caused by the accumulation of dental plaque. Dental plaque is a tough biofilm that contains harmful bacteria and forms in the mouth of any individual. These harmful bacteria can cause damage to the teeth and gums. If the plaque is not removed, it can lead to gum recession and the formation of periodontal pockets containing pus.
These periodontal pockets, along with the hardened dental calculus, make it difficult to remove plaque without dental professional support, and periodontitis will progress more severely. If not detected and treated promptly, periodontitis can destroy the entire supporting structure for the teeth, and even affect the underlying bone.
See more: Quick and Easy Methods for Tightening a Loose Tooth at Home
Signs of periodontal disease
Signs of periodontitis
- Red, swollen, and easily bleeding gums (when brushing or flossing)
- Receding gums
- Bad breath
- Formation of pus pockets between teeth and gums
- Loose or separated teeth
- Changes in the way teeth fit together when biting
- Denture wearers may notice changes in how their dentures fit compared to their natural teeth
- Periodontitis can progress from mild to severe. The initial stage is gingivitis, characterized by red, swollen, and uncomfortable gums. During this stage, gums may bleed when brushing or flossing.
As the disease progresses and directly affects the tooth sockets, pus pockets form, providing a favorable environment for bacteria to thrive. Dental calculus forms within these pockets and is not easily removed by regular oral hygiene measures. Advanced periodontitis requires deep dental cleaning to remove deposits from the gum pockets.
What is periodontitis?
If gingivitis is not treated properly, harmful bacteria continue to spread and affect the entire periodontal structure, leading to periodontitis. At this stage, the disease becomes more complicated to treat.
Signs of periodontitis:
- Formation of pus pockets in the gums
- Weakening of the tooth sockets, causing loose teeth
- Receding gums lead to exposed tooth roots and bad breath
- Bone loss around the tooth sockets, indicating a high risk of tooth loss
Effects of periodontal disease
Periodontitis is one of the oral diseases that have a very negative impact on the patient’s oral health:
- Bad breath, leading to a lack of confidence in communication
- Pain and discomfort, especially sensitivity to hot/cold foods
- Loss of taste, difficulty in eating, affecting the stomach
- Loose teeth, in severe cases, patients may face the risk of tooth loss.
How to treat periodontitis?
There are four basic types of treatment commonly used for periodontitis:
- Emergency treatment
- Non-surgical treatment
- Surgical treatment
- Maintenance treatment
Non-surgical treatment is the most commonly used method and involves two steps:
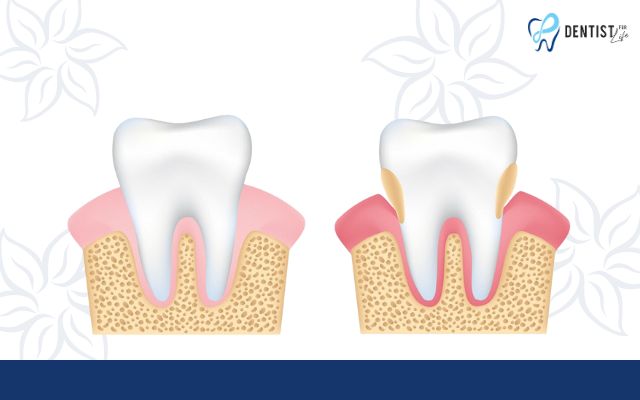
- Step 1: The dentist assesses factors favorable for plaque retention, impediments to oral hygiene, and controls bacterial plaque retention.
- Step 2: Elimination of factors favorable for plaque retention, hindering the development of harmful bacteria through various methods suitable for the patient’s dental condition:
- Scaling and root planing is a procedure indicated for all periodontitis treatment plans
- Repair or replacement of faulty dental fillings
- Repair or replacement of faulty dental restorations
- Evaluation and determination of teeth that need to be removed
- Stabilization of loose teeth
- Provision of temporary restorations when necessary
The method of treating periodontitis depends on the stage and severity of the disease. If periodontitis is detected early, when it is still in the gingivitis stage and has not affected the supporting structure under the teeth, patients will be instructed to improve daily oral hygiene after deep cleaning with scaling and root planing.
Although these simple methods have been applied, the condition of periodontitis becomes more severe, and treatment is necessary. The first step is special deep cleaning, commonly known as scaling and root planing. During this step, plaque and tartar are carefully removed from deep within the periodontal pockets.
This treatment process may extend over several appointments, depending on the patient’s periodontal condition. The tooth surfaces are cleaned and smoothed, creating conditions for healthy gum tissue to reattach to the tooth roots. This process is called “periodontal cleaning” or “deep cleaning” and often requires multiple appointments to complete.
See more: Understanding Gum Recession: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Care after periodontitis treatment
After completing periodontitis treatment, patients will be required to have regular follow-up appointments. Regular dental check-ups and deep cleaning are essential in controlling periodontitis. Depending on the case, the patient’s appointments will vary between a general dentist and a periodontist.
Thorough personal hygiene at home plays a crucial role in preventing the progression of periodontitis or the recurrence of the condition. Just a few minutes twice a day to brush and clean between teeth and gums. Daily oral hygiene helps control plaque buildup and reduces the likelihood of tartar formation.
The fear of tooth loss due to periodontitis will no longer be a concern if you maintain a habit of brushing, cleaning between teeth, following a proper diet, and regularly checking your oral health. A clean and healthy set of teeth is within reach!
There is a close relationship between periodontal disease and overall health
The mouth is considered the gateway to overall body health. It reflects signs of malnutrition or general infection. For instance, systemic diseases—those affecting overall health such as diabetes, AIDS, and autoimmune disorders—can be caused by oral lesions or other oral diseases.
The mouth is a hiding place for billions of bacteria, many of which are the cause of tooth decay and gum diseases. Researchers have indicated that advanced periodontitis (a severe condition affecting the tooth-supporting structures) may be closely related to health issues such as heart disease, stroke, and pneumonia, among others. Additionally, pregnant women with periodontal disease may face the risk of preterm birth and/or low birth weight babies.
Further in-depth research is needed, but many researchers suspect that bacteria and related infections from periodontal disease are the cause of systemic diseases. Similar to diabetes, blood cell disorders, HIV, and AIDS, they may compromise the immune system, making periodontal disease more severe. Some studies have outlined an undeniable connection between chronic inflammation from periodontal disease and the progression of heart disease.
See more: What Does a Cavity Look Like? Signs and Symptoms You Need to Know
Advice from your dentist
At Dentist For Life in Ohio, we recognize the critical role of periodontics in preserving overall oral health. Understanding the significance of gum and jaw health, our commitment extends to comprehensive care, ensuring our patients receive the utmost attention and expertise.
Periodontics is integral in our approach to maintaining healthy smiles, and our skilled professionals are dedicated to providing tailored treatments that prioritize the wellness of gums and supporting structures.
Trust Dentist For Life for personalized care and solutions aimed at fostering optimal periodontal health, contributing to the longevity and vitality of your smile. Schedule a consultation today to experience our commitment to exceptional periodontal care.